We covered The Pyramid of pain concept used in incident response and threat hunting which covers the artifacts of the attacker’s tools and techniques and how easy/difficult on them to change to avoid detection by analysts. We also covered and explained what every layer in the pyramid represents as an artifact during the stage of a cyber attack. This was part of TryHackMe The Pyramid of pain.
Challenge Description
Learn what is the Pyramid of Pain and how to utilize this model to determine the level of difficulty it will cause for an adversary to change the indicators associated with them, and their campaign.
Pyramid of Pain Overview
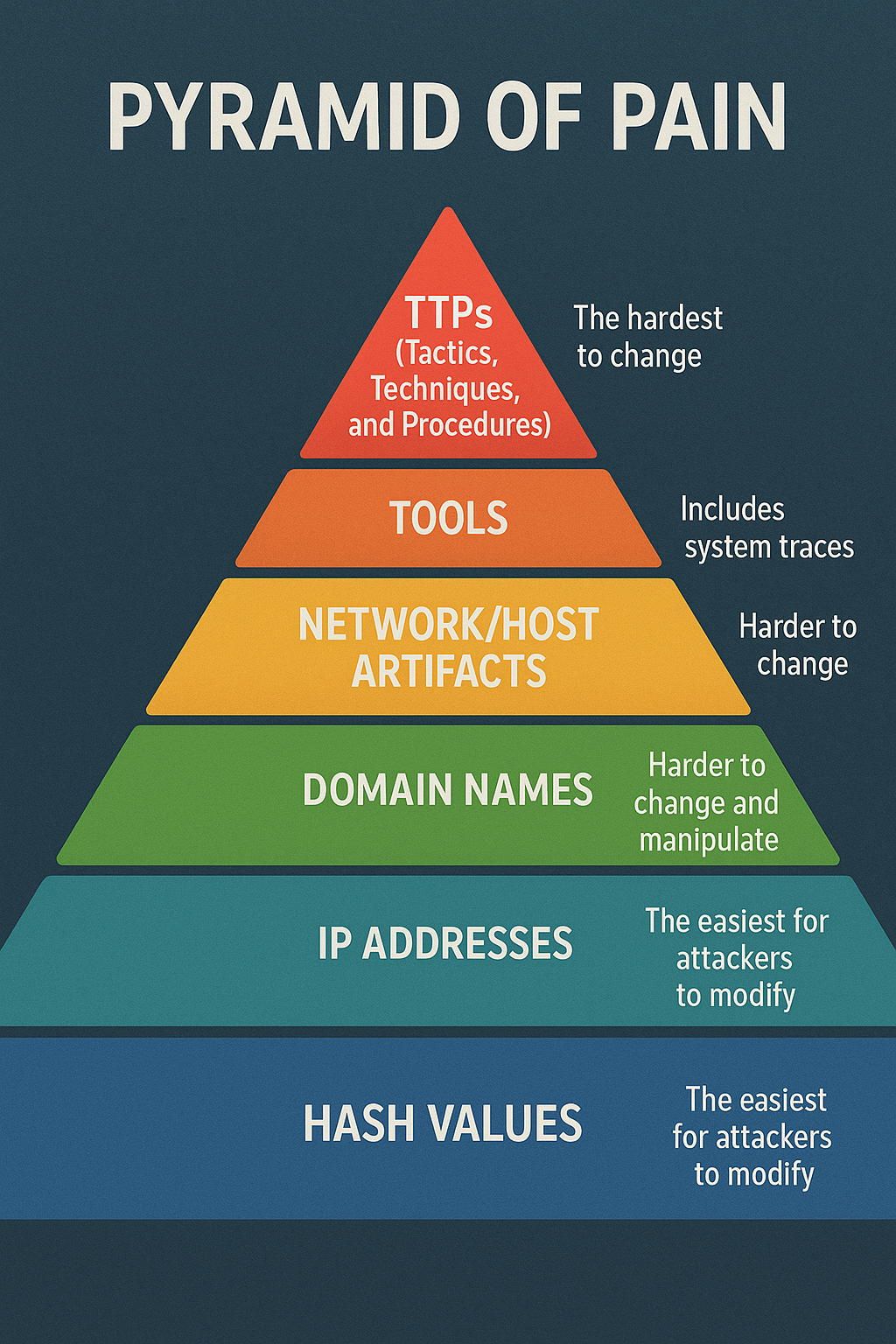
The pyramid is a model representing different types of attack artifacts, arranged by the difficulty it takes for an attacker to change them. From bottom to top, the levels are:
- Hash Values: The easiest for attackers to modify.
- IP Addresses: More difficult but still relatively easy to change.
- Domain Names: Harder to change and manipulate.
- Network/Host Artifacts: Includes system traces like registry changes or user agent strings.
- Tools: Software attackers use to infiltrate systems.
- TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures): The hardest to change as it defines the attackers’ behavior and methods.
Practical Example – Hash Values:
A report from VirusTotal is shown with a file labeled as malicious due to its hash. However, it’s explained that changing a hash is very easy for an attacker. They can simply add a string to the file, creating a new hash. This demonstrates why hash values are at the bottom of the pyramid.
IP Addresses
A report from the ANY.RUN sandbox shows how malware communicates with command-and-control (C2) servers through HTTP requests to IP addresses.Attackers can change or rotate IP addresses using techniques like Fast Flux, where a domain name resolves to multiple IPs to hide the C2 server. Although more difficult than changing a hash, it’s still relatively simple for attackers.
Domain Names
Domain names, though harder to change than IPs, can still be manipulated. Attackers may use techniques like Punycode attacks, where they register domain names with Unicode characters to mimic legitimate domains (e.g., “adidas.com” can be faked as “addïdas.com”).
URL shortening is another method attackers use to hide malicious domains.
Network and Host Artifacts
These include system traces such as changes to the registry or network communications, which are left behind after an attack. These are harder for attackers to alter without detection.
TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures)
The top of the pyramid represents the attacker’s overall behavior, such as how they conduct phishing or lateral movement in a network. This is the hardest to change because it requires altering their entire strategy.
Threat Hunting TryHackMe | The Pyramid of Pain | Room Answers
What term refers to an address used to access websites?
What type of attack uses Unicode characters in the domain name to imitate the a known domain?
A security vendor has analysed the malicious sample for us. Review the report here to answer the following questions.
The actor drops a malicious executable (EXE). What is the name of this executable?
Look at this report by Virustotal. How many vendors determine this host to be malicious?
How many POST requests are in the screenshot from the pcap file?
Provide the alternative name for fuzzy hashes without the abbreviation
Chimera is a China-based hacking group that has been active since 2018. What is the name of the commercial, remote access tool they use for C2 beacons and data exfiltration?




