This article explores how artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the employment landscape, particularly within cybersecurity and automation. It discusses both the opportunities and disruptions brought by AI across different sectors.
Historical Shifts in Employment
Technological revolutions—from agricultural mechanization to industrialization and the information age—have consistently displaced certain types of jobs while giving rise to new ones. The transition from farming to factory work, and later to IT roles, illustrates how societies adapt, with workers shifting to roles requiring different skills. AI is the next wave in this evolution.
Elimination and Creation: AI’s Dual Impact
Like the shift from candle makers to electric lighting, AI will remove some roles but also liberate humans to pursue more creative, strategic, and rewarding work. It’s not job loss, but job transformation.
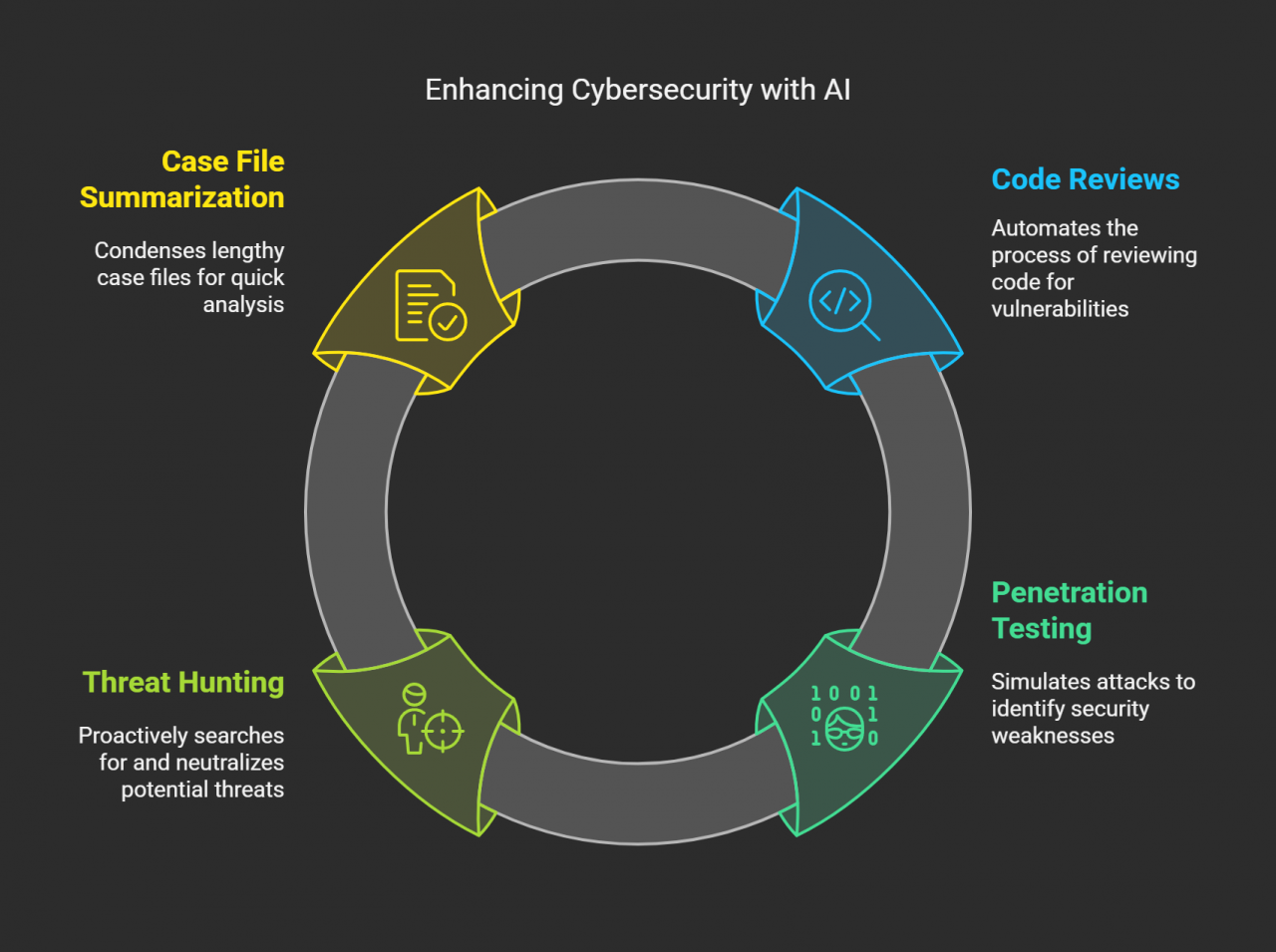
AI’s Positive Disruption in Cybersecurity
AI streamlines time-intensive cybersecurity tasks. It can automate code reviews, penetration testing, and threat hunting. Summarizing long case files becomes effortless, giving security teams more time to focus on high-level work.
Generative AI Enhances Creativity and Scale
AI proposes novel hypotheses during threat hunts and deciphers complex logs using its language model capabilities. It can also recommend mitigation strategies, serving as an intelligent assistant that scales human expertise.
Executive Support through AI
For executives, AI can scan threat advisories, identify indicators of compromise, and run federated searches across enterprise systems. The result: a clear answer to “Am I affected?”—without drowning in technical noise.
AI: The Hacker’s Tool Too
Just as AI aids defenders, attackers harness it for automating reconnaissance, scanning vulnerabilities, and crafting sophisticated phishing emails. Generative AI eliminates grammatical red flags, making phishing harder to detect.
Social Engineering Gets Smarter
Deepfakes and personalized disinformation are now realistic threats. Attackers use AI to simulate voices and videos of trusted individuals—leading to real-world financial and data losses.
Smarter Password Cracking and Exploit Generation
AI can learn from leaked password databases and generate smarter guesses. It can also write exploit code and malware, lowering the technical barrier for cybercriminals.
A New Attack Surface
As AI becomes more integrated into cybersecurity infrastructure, it also becomes a new vector for attacks. Organizations must now defend both traditional systems and their AI-driven counterparts.
AI Use by Cybersecurity Professionals
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI is streamlining daily workflows like code reviews, penetration testing, and case summarization. These tasks, which often consumed hours of manual effort, can now be automated for efficiency and speed.
Threat Hunting & Hypothesis Generation
Cybersecurity experts use AI to hypothesize possible intrusion paths and identify indicators of compromise. AI suggests creative scenarios that may not be immediately obvious to human analysts.
Log Interpretation and Anomaly Detection
AI helps in parsing and explaining complex logs, such as SQL commands. It detects outliers—behaviors that deviate from the norm and may indicate malicious activity.
Strategic Decision Support
Executives rely on AI to digest cybersecurity advisories and assess exposure across their systems. The AI answers critical questions like “Am I affected?” with speed and precision.
Virtual Subject Matter Experts (SMEs)
Chatbots powered by AI provide on-demand cybersecurity guidance, emulating certified experts like CISSP holders.
AI Use by Cybercriminals
Automated Reconnaissance & Exploits
Attackers use AI to scan networks for vulnerabilities and to adaptively exploit systems, simulating intelligent intrusion behavior.
Smarter Phishing
Generative AI writes flawless emails in any language, eliminating typical phishing red flags like poor grammar or misspellings.
Deepfakes & Social Engineering
Video and audio deepfakes mimic real individuals convincingly, enabling sophisticated scams and impersonation attacks.
Disinformation Campaigns
AI is used to create and spread convincing fake news, which can destabilize organizations and societies by sowing confusion.
Password Cracking & Malware Development
AI predicts passwords based on leaked data and even generates exploit and malware code from descriptive prompts, reducing the skill needed to launch attacks.
Cybersecurity Skills Still in Demand
The market urgently needs professionals skilled in architecture, threat modeling, and strategic planning. Roles requiring deep critical thinking will flourish, as AI complements rather than replaces human intellect.
What roles humans will still be needed for in an AI-driven cybersecurity world?
Despite AI’s powerful capabilities, the video strongly emphasizes that humans remain indispensable in cybersecurity. Here are the key roles and responsibilities where human expertise continues to be essential:
Strategic Thinking and Planning
- AI can execute tasks but doesn’t define goals. Humans are responsible for setting the direction, deciding what needs to be done, and planning responses to emerging threats.
- Roles like security architects, CISOs, and strategists are irreplaceable because they align cybersecurity practices with organizational objectives.
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making
- AI offers suggestions, but not all are sound. Humans must critically evaluate AI-generated insights and decide which actions to take.
- Professionals must assess whether an AI’s recommendation aligns with reality, ethics, and broader organizational goals.
Handling Unpredictable Scenarios (Black Swan Events)
- AI relies on patterns from existing data. When facing novel, rare, or unprecedented threats, human intuition and experience are key.
- Analysts and incident responders are needed to recognize and adapt to unexpected attack patterns that AI might miss.
Problem Solving in Complex Contexts
- While AI can mimic reasoning, real-world problem solving—especially in dynamic and high-pressure environments—requires human oversight.
- Humans excel at creative, contextual, and lateral thinking, which is critical in adversarial scenarios.
Ethics and Judgment
- AI lacks a moral compass. Humans must govern AI’s use, ensuring it aligns with privacy laws, organizational policies, and ethical standards.
- Roles in governance, compliance, and ethics become even more important in an AI-augmented future.
Higher-Order Creative Roles
- As AI takes over routine tasks, human roles evolve toward designing solutions, inventing new security protocols, and building resilient systems.
Insights Based on Numbers
AI as a ‘fulcrum’ or ‘force multiplier’: This metaphor illustrates AI’s potential to amplify the productivity of a limited workforce, vital for countering modern cyber threats.
400,000+ Cybersecurity Job Openings in the U.S. alone highlight the continued demand for skilled professionals, underscoring AI’s role as a support, not a replacement.
1 open job per 3 workers in cybersecurity shows a massive shortage, reaffirming the necessity of human expertise alongside AI.
Conclusion
AI is not replacing humans—it is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape. By offloading repetitive, data-heavy tasks to machines, AI amplifies human capacity to focus on creativity, strategy, and judgment. While attackers are also leveraging AI, this arms race only magnifies the need for skilled professionals who can adapt, anticipate, and lead.
The ultimate takeaway? We still need humans in the loop. Their critical thinking, ethical oversight, and innovative instincts are irreplaceable. In a world of increasing complexity and cyber threats, AI is the lever—but humans remain the force behind the defense.




