“Every second, your organization’s data is under attack. Who’s watching? The Security Operations Center (SOC), a dedicated team monitoring and defending against cyber threats around the clock. In this article, we dive into the basics of SOCs and how they play a pivotal role in protecting your data from unseen attackers. We also covered the room answers for TryHackMe SOC Fundamentals room.
Core Responsibilities of a SOC Team
The SOC team’s responsibilities can be broken down into several key areas:
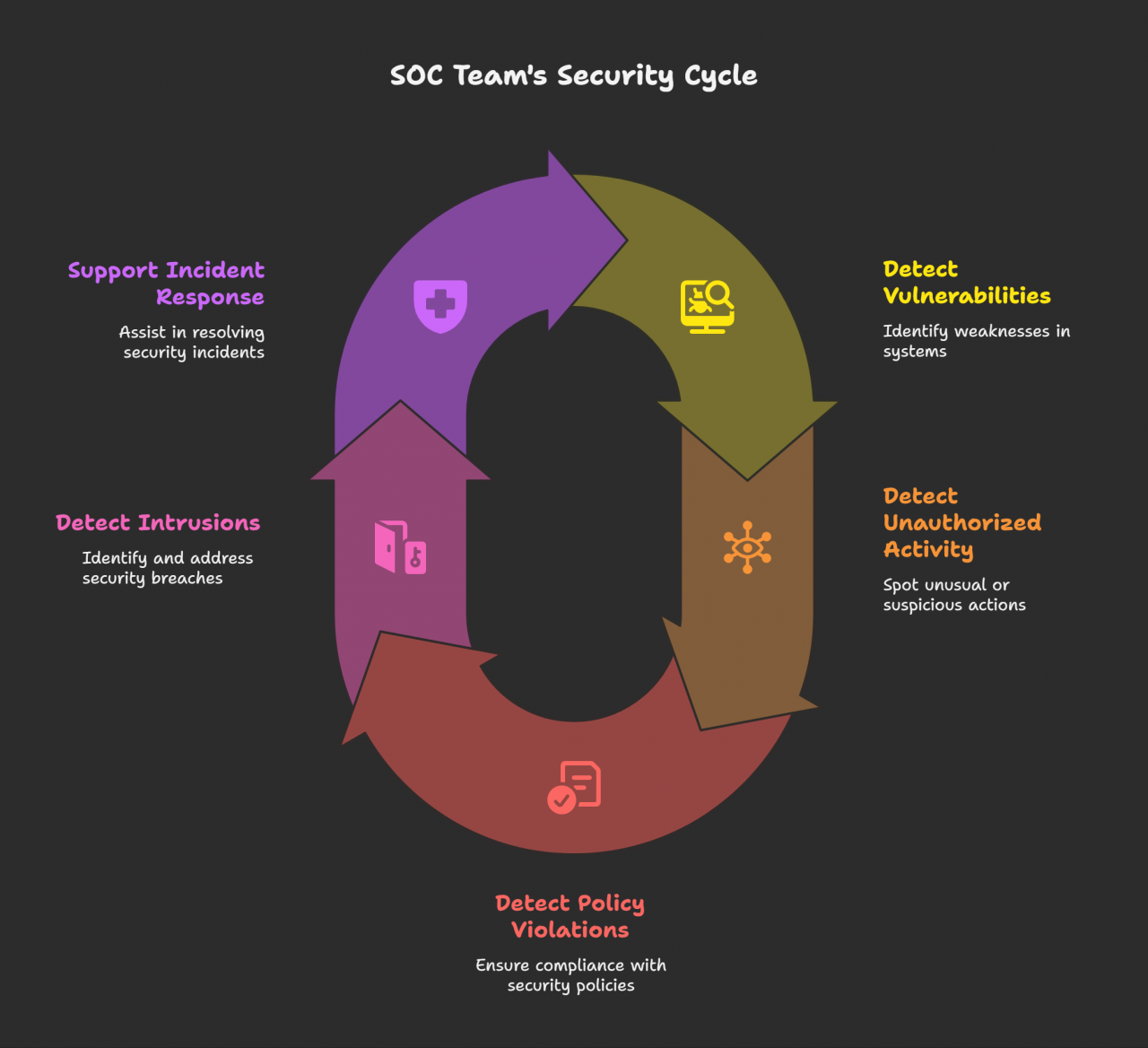
- Detecting Vulnerabilities: While not their sole responsibility, SOC teams are heavily involved in identifying and addressing system weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
- Identifying Unauthorized Activity: A crucial part of their role is to monitor for any suspicious login attempts or unauthorized access to the organization’s network and resources.
- Enforcing Security Policies: SOC teams ensure that all security policies are being followed and that there are no breaches in the established protocols for resource usage.
- Detecting Intrusions: If unauthorized activity goes undetected, it can lead to a network breach. The SOC team is tasked with identifying these intrusions before significant damage can occur.
- Incident Response: When an intrusion or exploitation is detected, the SOC team works in tandem with the incident response team to contain the threat, fix vulnerabilities, and minimize the impact of the breach.
The SOC Team’s Workflow
This process begins with alerts generated by a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution, such as Splunk or IBM QRadar.
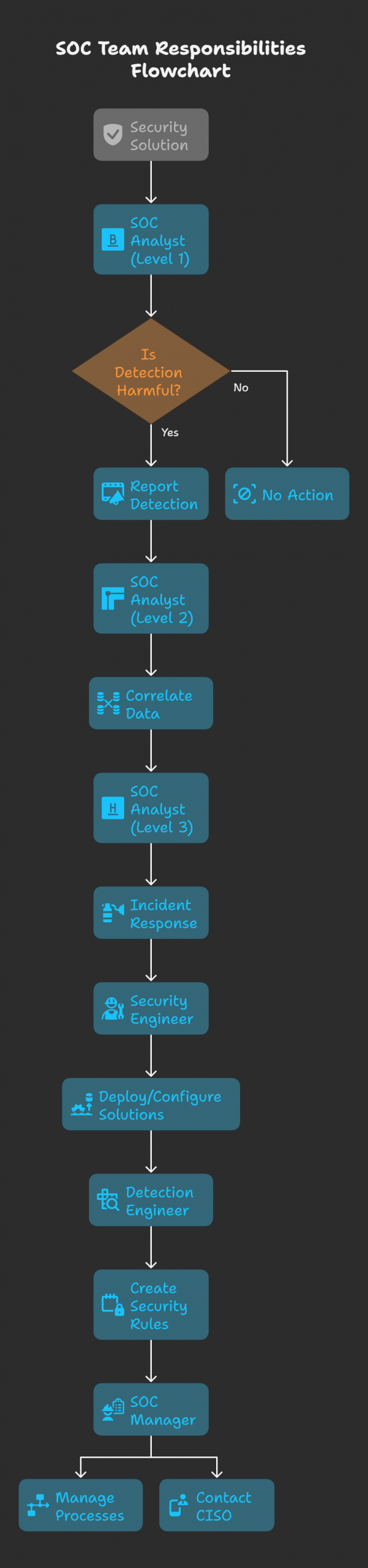
- Level 1 SOC Analyst: These analysts are the first line of defense. They investigate the alerts from the SIEM, performing initial triage to determine if an alert represents a real security incident. If it’s a genuine threat, it gets escalated to a Level 2 analyst. Otherwise, the alert is discarded.
- Level 2 SOC Analyst: The Level 2 analyst conducts a more in-depth investigation, correlating data from various sources to confirm the incident. For instance, they might compare web server logs with firewall logs to get a complete picture. If the incident is confirmed, it is escalated to Level 3.
- Level 3 SOC Analyst: These senior analysts are responsible for initiating the incident response cycle, which includes containing the threat, eradicating it from the system, and recovering any affected data or systems.
- Security Engineers: This team is responsible for deploying and configuring the security tools that the SOC team uses, such as the SIEM, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions, and firewalls.
- Detection Engineers: These specialists create and refine the security rules within the SIEM to ensure that alerts are generated accurately and efficiently.
- SOC Manager: The SOC Manager oversees the entire operation, managing the team and reporting to the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO).
The Alert Triage Process
When a Level 1 analyst receives an alert, they follow a structured process to determine its severity and priority. This involves answering the “Five W’s”:
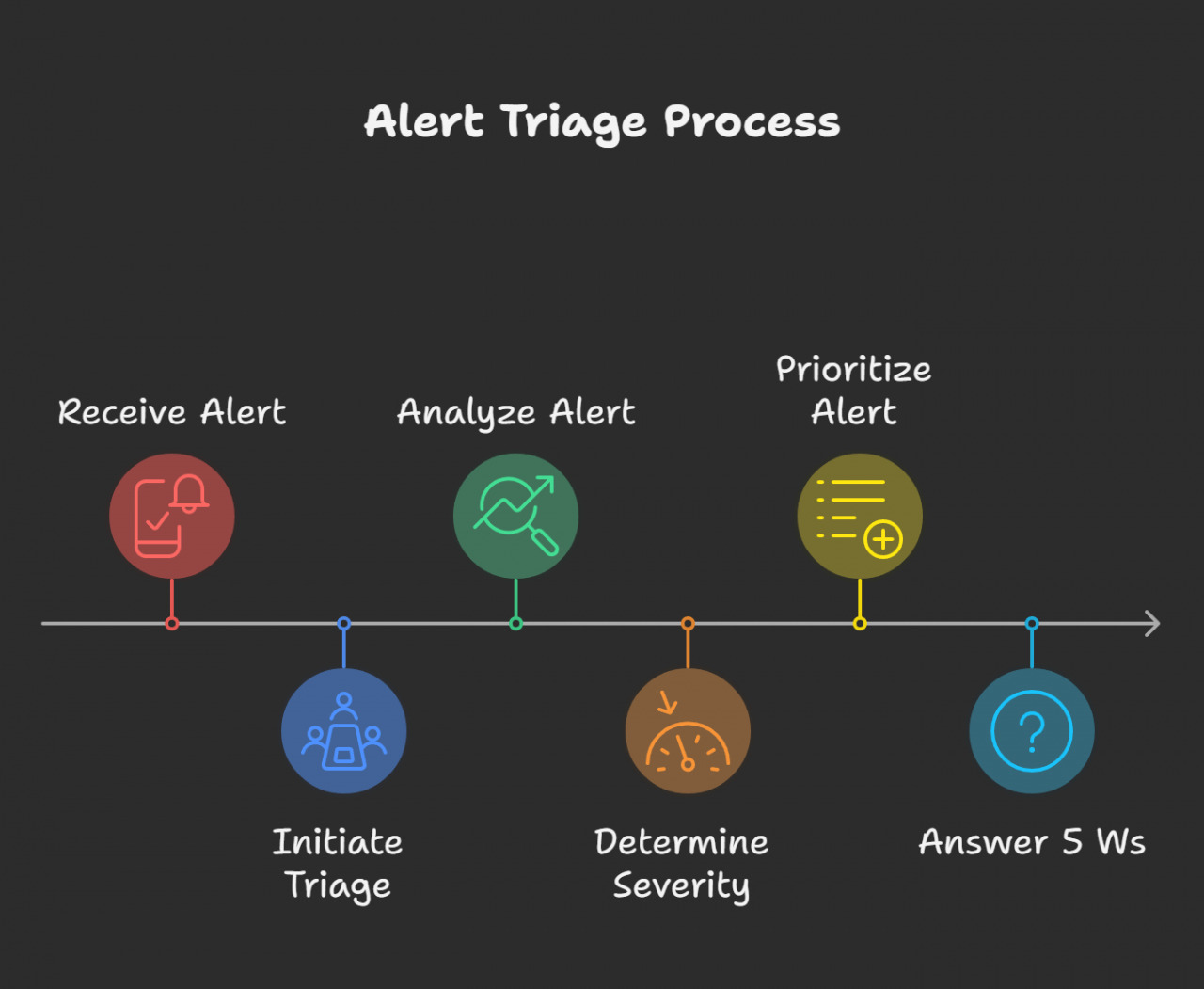
- What: What is the nature of the alert? (e.g., malware detected)
- When: When did the activity occur?
- Where: What system or network segment is affected?
- Who: Who or what initiated the activity? (e.g., a specific user, malware, or an attacker)
- Why: What is the reason for this activity? This question is answered after a thorough investigation.
Essential Tools of the Trade
The SOC team relies on a variety of powerful tools to protect the organization:
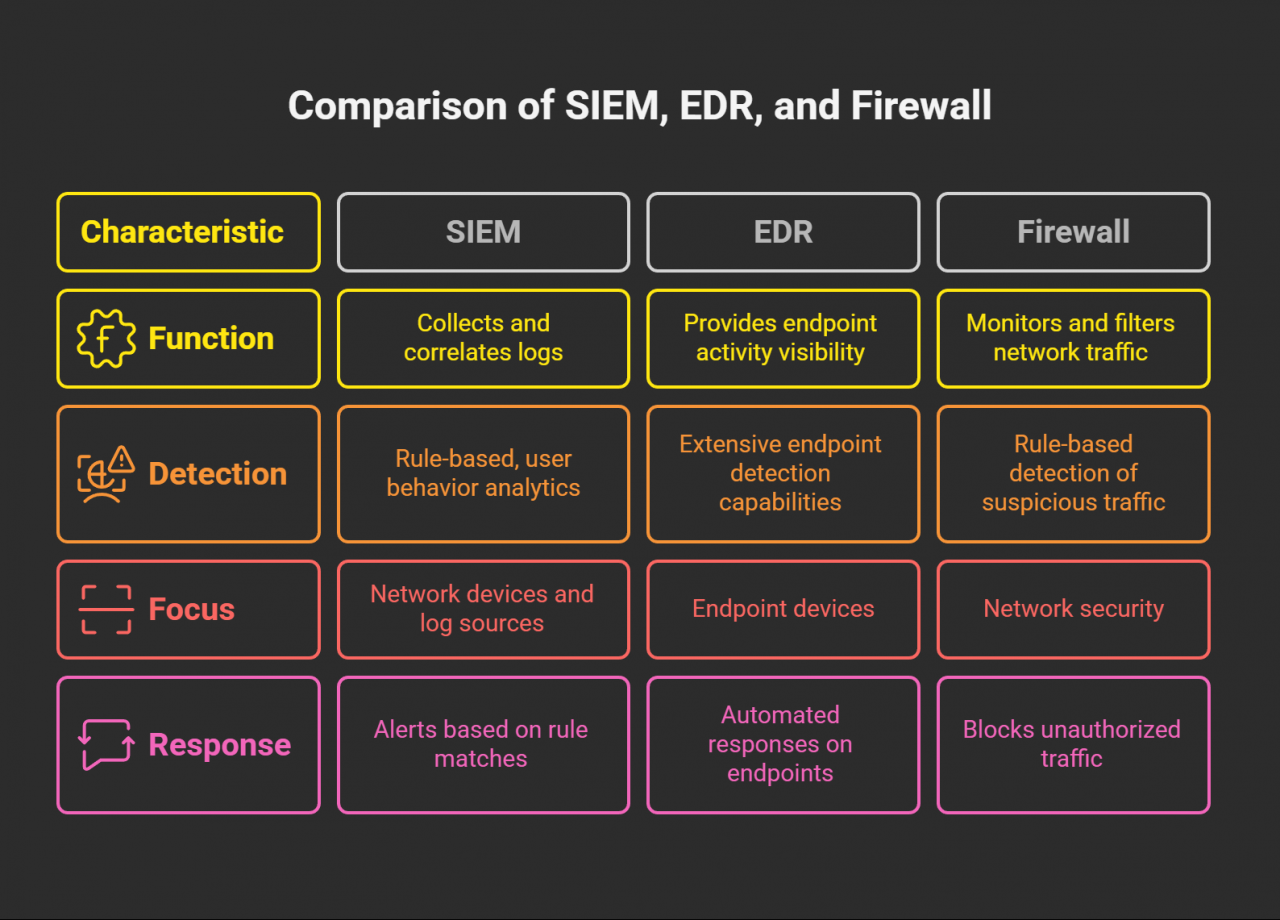
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): This is the heart of the SOC. It collects and correlates logs from numerous sources, generates alerts, and allows for the configuration of security rules.
- EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response): EDR solutions provide protection and visibility for individual endpoints like computers and servers. They can be configured for automated responses, such as blocking malicious files.
- Firewall: The firewall is the network’s gatekeeper, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to block suspicious activity based on a set of predefined rules.
TryHackMe SOC Fundamentals Room Answers
What does the term SOC stand for?
Security Operations Center
The SOC team discovers an unauthorized user is trying to log in to an account. Which capability of SOC is this?
Detection
What are the three pillars of a SOC?
People, Process, Technology
Alert triage and reporting is the responsibility of?
SOC Analyst (Level 1)
Which role in the SOC team allows you to work dedicatedly on establishing rules for alerting security solutions?
Detection Engineer
At the end of the investigation, the SOC team found that John had attempted to steal the system’s data. Which ‘W’ from the 5 Ws does this answer?
Who
The SOC team detected a large amount of data exfiltration. Which ‘W’ from the 5 Ws does this answer?
What
Which security solution monitors the incoming and outgoing traffic of the network?
Firewall
Do SIEM solutions primarily focus on detecting and alerting about security incidents? (yea/nay)
yea
What: Activity that triggered the alert?
Port Scan
When: Time of the activity?
June 12, 2024 17:24
Where: Destination host IP?
10.0.0.3
Who: Source host name?
Nessus
Why: Reason for the activity? Intended/Malicious
Intended
Additional Investigation Notes: Has any response been sent back to the port scanner IP? (yea/nay)
yea
What is the flag found after closing the alert?
THM{000_INTRO_TO_SOC}




