How to Review a Vulnerable SQL Injection Login Form in PHP
We reviewed a login form written in php and vulnerable to SQL Injection. We compared different versions of the code and built a SQL Injection payload for each case.
First Code Review
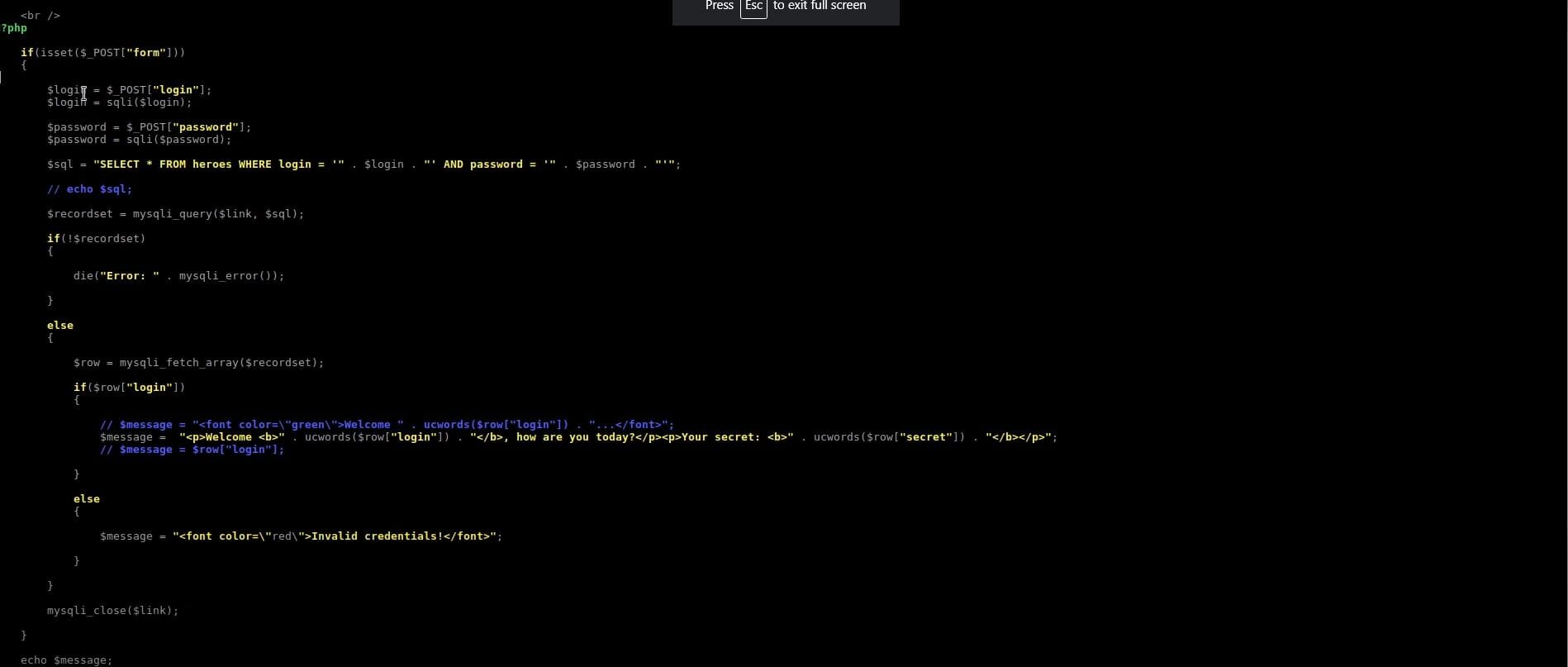
The code is a php code for login form. As we can see, the login username and login password are stored in two variables. The value of each variable is taken as an input from the user via HTTP POST request.
The problem here is that whatever the user enters in the login form, it is directly used in the sql query in the following line and then executed in the backend allowing for malicious input to take place.
Exploitation
The following screenshot illustrates how we injected a SQL payload into the login form
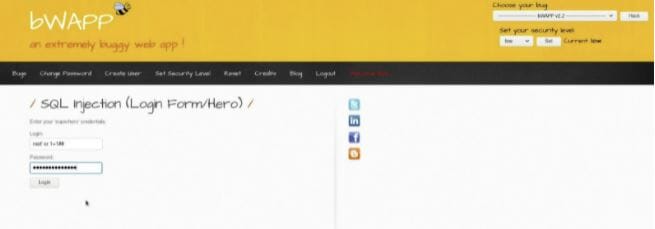
We can try different payload variations such as
root’ or 1=1##
‘ or 1=1 — #
‘ or 1–
As long as the login fields variables aren’t used with single quotes. We will see code examples were the variables are quoted. In those cases, the SQL injection payload would differ.
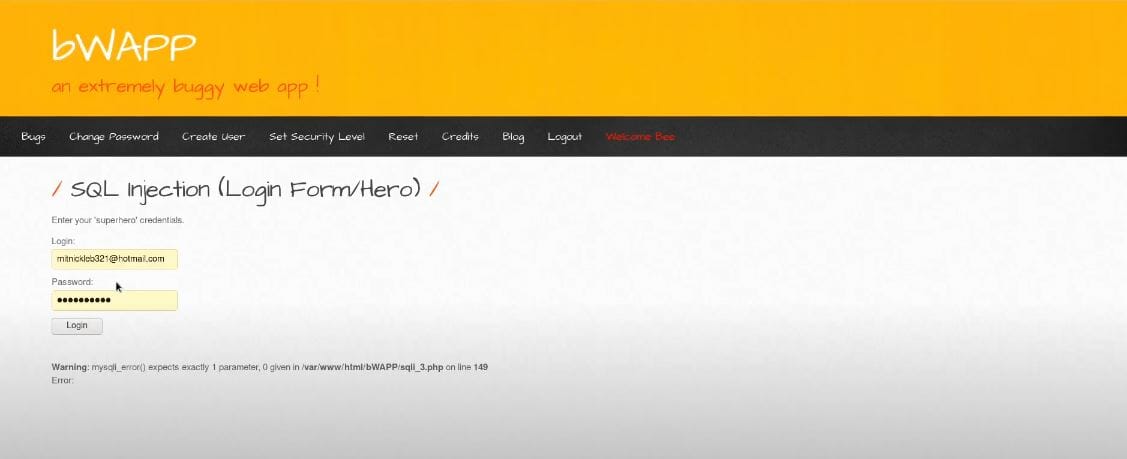
The screenshot below demonstrates successful exploitation of the login form.
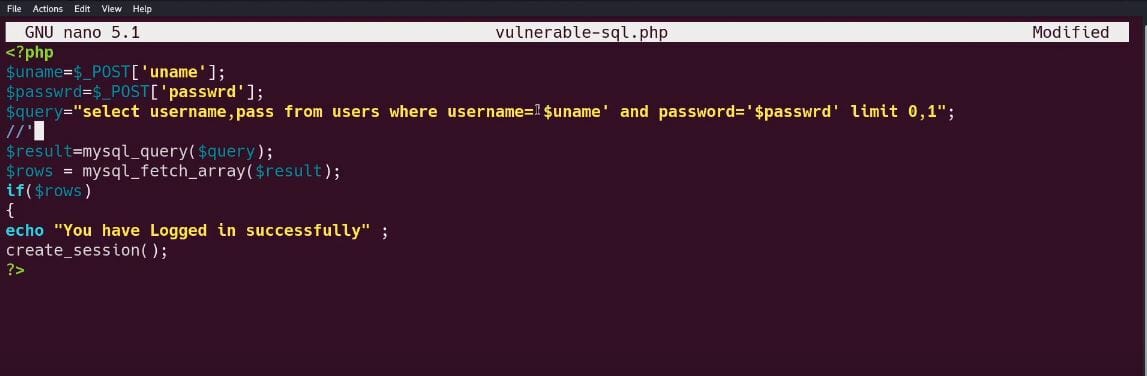
Second Code Examination
In the following screenshot, we reviewed another vulnerable php login form to SQL Injection. The difference is that the login variables are used with single quotes in the query variable
Thus our SQL payload would differ. Our payload in this case should start and end with a quote to close the ones used in the query variable.
Example would be:
‘ or ”=’
‘root or ”=’
Third Code Review
We modified the same code to use parentheses with single quotes in the SQL query.
In this case, our SQL Payload would also need to start with single quote and a parentheses
‘) or true–
Fourth Code examination
What if the code contained the two login variables with parentheses and double quotes.
Our SQL payloads in this case need to close the parenthesis and the double quotes
” or true–
“) or true–
‘)) or true–
Full Video Walk-Through




